pacman::p_load(sf, sfdep, tmap, tidyverse)In-class_Ex06
Installing and Loading the R packages
Before we get started, we need to ensure that sfdep, sf, tmap and tidyverse packages of R are currently installed in your R.
The Data
For the purpose of this in-class exercise, the hunan data sets will be used. There are two data sets in this use case, they are:
- Hunan, a goaspatial data set in ESRI shapefile format, and
- Hunan_2021, an attribute data set in csv format.
Importing geospatial data
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/Geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`C:\Users\kwekm\Desktop\SMU Year 3 Semester 2\IS415 Geospatial Analytics and Applications\KMRCrazyDuck\IS415-KMR\In-class_Ex\Data\Geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Import csv file into r environment
hunan2012 <- read_csv("data/Aspatial/Hunan_2012.csv")Performing relational join
The code chunk below will be used to update the attribute table of hunan’s SpatialPolygonsDataFrame with the attribute fields of hunan2012 dataframe. This is performed by using left_join() of dplyr package.
hunan_GDPPC <- left_join(hunan,hunan2012)%>%
select(1:4, 7, 15)tmap_mode("plot")
tm_shape(hunan_GDPPC) +
tm_fill("GDPPC",
style = "quantile",
palette = "Blues",
title = "GDPPC") +
tm_layout(main.title = 'Distribution of GDP per capita by distribution',
main.title.position = "center",
main.title.size = 1.2,
legend.height = 0.45,
legend.width = 0.35,
frame = TRUE) +
tm_borders(alpha = 0.5) +
tm_compass(type="8star", size = 2) +
tm_scale_bar() +
tm_grid(alpha =0.2)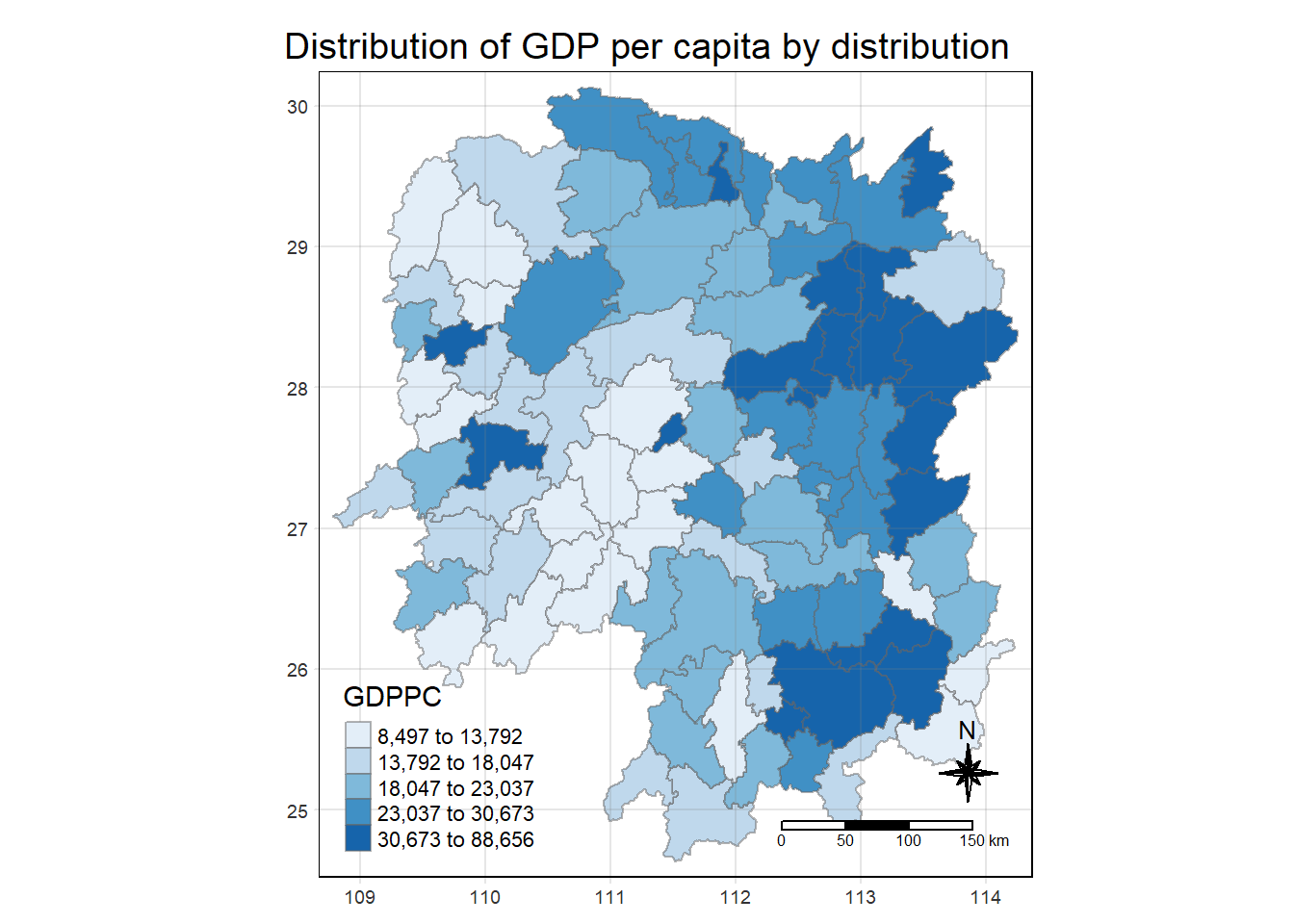
Visualising Regional Development Indicator
Now, we are going to prepare a basemap and a choropleth map showing the distribution of GDPPC 2012 by using qtm() of tmap package.
basemap <- tm_shape(hunan_GDPPC) +
tm_polygons() +
tm_text("NAME_3", size=0.5)
gdppc <- qtm(hunan_GDPPC, "GDPPC")
tmap_arrange(basemap, gdppc, asp=1, ncol=2)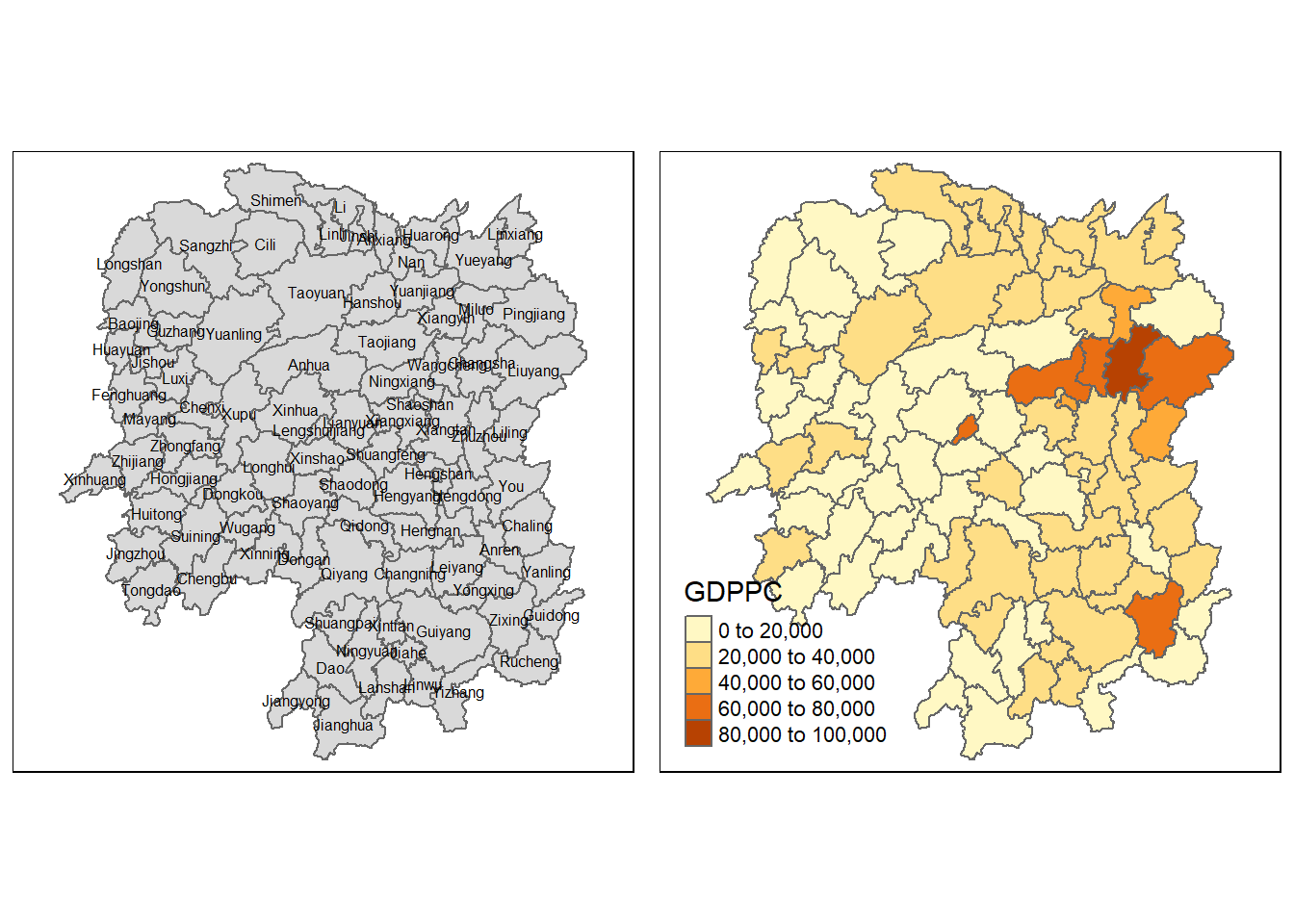
Contingency neighbours method
In the code chunk below, st_contiguity() is used to derive a continguity neighbour list by using queen’s method.
cn_queen <-hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
.before = 1)derive a contiguity neighbour list Using Rook’s method
cn_rook <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb =st_contiguity(geometry),
queen =FALSE,
.before = 1)